Phenols Test Kits
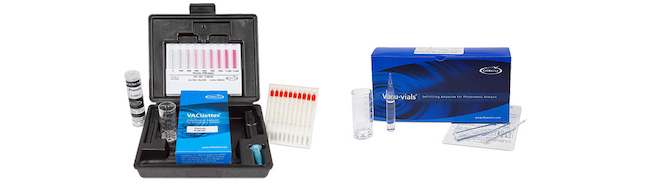
Visual Kits
| Range | MDL | Method | Type | Test Kit | Refill |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 - 1.0 & 0 - 12 ppm | 0.05 ppm | 4-Aminoantipyrine | CHEMets | K-8012 | R-8012 |
| 0 - 300 ppm | 25 ppm | 4-Aminoantipyrine | HR CHEMets | K-8020D | R-8012 |
Photometric Kits
| Range | Method | Type | Test Kit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 8.00 ppm | 4-Aminoantipyrine | Vacu-vials | K-8003 |
| 0 - 20.0 ppm | 4-Aminoantipyrine | Vacu-vials | K-8023 |
The CHEMetrics test kits for the determination of Phenols in aqueous solutions employ the 4-Aminoantipyrine method, delivering sensitivity and accuracy within two minutes or less. Based on CHEMetrics patented Self-Filling Reagent Ampoule technology. Premixed. Premeasured. Precise. Each kit contains 30 tests. Visual and instrumental phenols testing kit formats span low and high measurement ranges. CHEMets® and HR CHEMets® visual test kits use colour comparators for analysis while Vacu-vials® instrumental kits rely on CHEMetrics direct-readout photometers or spectrophotometers capable of accepting a 13-mm diameter round cell. Suitable for potable water testing.
The Phenols Vacu-vials test kits K-8003 and K-8023 can be used with a Hach DR900 Colorimeter in conjunction with the CHEMetrics DR900 Vacu-vials® Adapter, Cat. No. A-0215. No endorsement by Hach Company is implied or intended.
4-Aminoantipyrine Method
CHEMetrics' phenols kits employ the well-established 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AAP) method. Phenolic compounds react with 4-AAP in alkaline solution in the presence of ferricyanide to produce a red reaction product. Phenol, meta-, and ortho-substituted phenols, and some para-substituted phenols, under proper pH conditions, are detected with this method. The method is applicable to the monitoring of phenolic compounds in wastewater. Results are expressed as ppm (mg/l) phenol.
References:
APHA Standard Methods, 14th ed., Method 510 C (1975).
ASTM D 1783-01, Phenolic Compounds in Water.
|
|
Technical Data Sheet |
Applications
Phenol itself is a common ingredient of disinfectants. In drinking or potable water, low-level phenolic concentrations impart a foul taste and odour, especially upon chlorination. High phenol concentrations can indicate contamination from industrial effluents or waste discharge. Phenol also has a long history as an antiseptic agent.
What is Phenol?
Phenol (a.k.a. hydroxybenzene or carbolic acid) is the simplest of a group of similar organic chemicals, which includes cresols, xylenols, and catechols. It is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH, consisting of a phenyl group (carbon ring) bonded to a hydroxy group (-OH). It is mildly acid and is corrosive to the eyes, skin and respiratory tract, and long term exposure can affect the kidneys and liver.